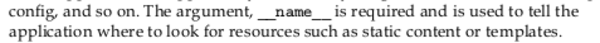- This book will teach you on how to build fully featured web applications with database integration.
- Also with making REST service.

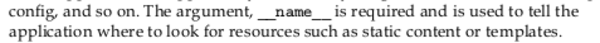
- The name of application variable is usually
app.
- The argument
__name__ is used to tell the application where to look for resource (for example, static contents or templates).

- Flask can handle basic routing as well.

- There is this
urlparse library to verify whether a string is a valid URL path or not.
- Above image is a simple example of the implementation of the
urlparse.

- This book uses Python 2.x.
- Python 2.x is usually default in Linux distribution.

- Some packages that need to be installed,
sudo apt-get install python-dev python-pip.
- The author of this books uses Linux Mint, hence the packages comes from Linux Mint repository.
pip is the package manager for Python. Similar to NPM of NodeJS.

- Install virtual environment so that the dependencies of the project is exclusive to the virtual environment and are not system wide.
sudo pip install virtualenvwrapper
echo "source /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh" >> ~/.bashrc

- Example command on how to make Python virtual environment and then install Flask.
mkvirtualenv hello
pip install flask
- However this is my preferred ways to install and use Python virtual environment.
- Install Python virtual environment using
pip with sudo pip install virtualenv.
- Or, in Ubuntu you can install it from the Ubuntu repository,
sudo apt-get install python-virtualenv.
- The to make the Python virtual environment.
mkdir project_name
cd project_name
virtualenv venv
. venv/bin/activate
pip install flask
. venv/bin/activate is used to go inside the virtual environment.- To go out from the virtual environment use this command
deactivate.

- This book method on how to use Python virtual environment.

- Use
# coding:utf-8 in the beginning of the Python entry file (usually main.py) to tell Python to use utf-8 encoding.
- This helps you to prevent nasty bugs exists within the application.